What and Why?
A while ago I had seen someone show all their winnings from using a twitter bot to retweet tweets. Today is a bit more advanced and now people ask to like, follow and sometimes tag. This bot does not tag others but it does retweet, like and follow people mentioned in the tweet.
Setup
First, make sure you have python installed and that you have setup pip.
If you haven't, create a new twitter account. If you want to use an existing one, be aware that this will spam the shit out of your account.
Installing Tweepy
So now that you have set up pip, you can use it to install tweepy easily. Open up cmd and execute the command pip list tweepy. Make sure the output doesn't have any errors and that it states that it was installed successfully.
Open up IDLE and execute the following line. If no errors appear, it was installed correctly.
import tweepy
Getting the API Keys
Now we need to create a twitter app. This may put some people off but don't stop here, it's very little effort.
Go to https://apps.twitter.com/ and click "Create New App"

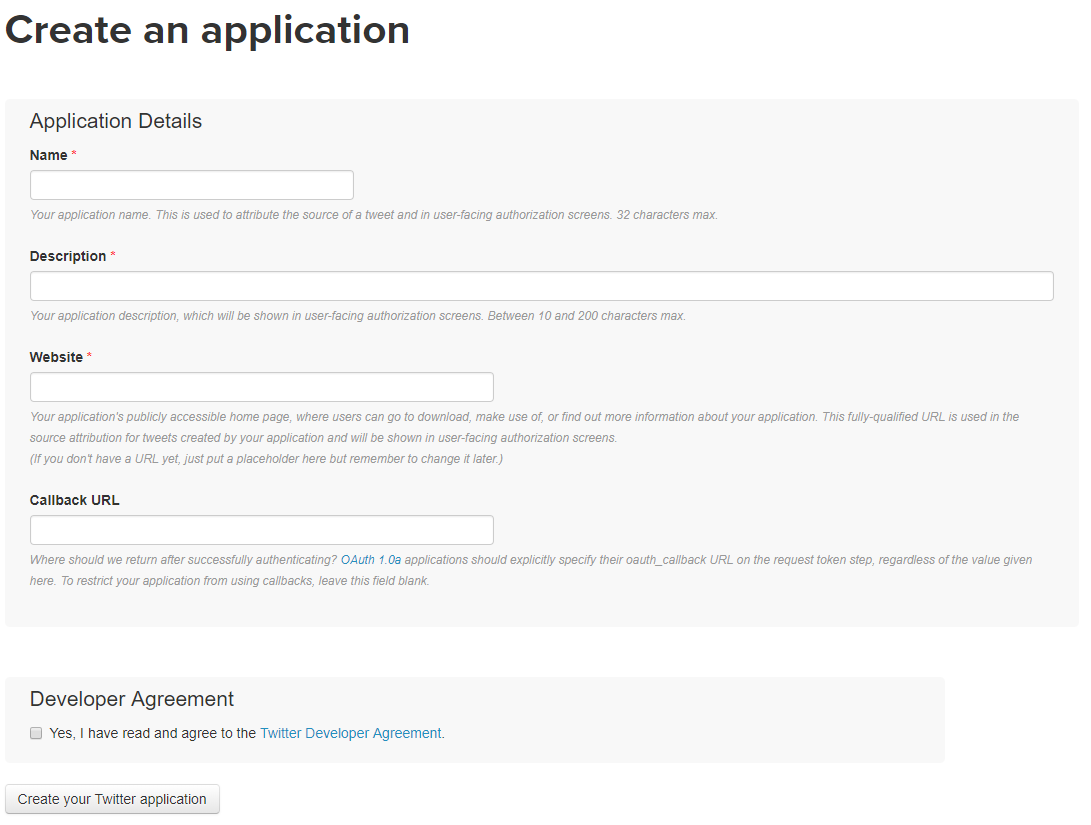
Fill in the form that is now provided and click "Create your Twitter application"
Now go to the "Keys and Access Tokens" tab and find the following keys as shown in the image below: - Consumer Key (API Key) - Consumer Secret (API Secret) - Access Token - Access Token Secret
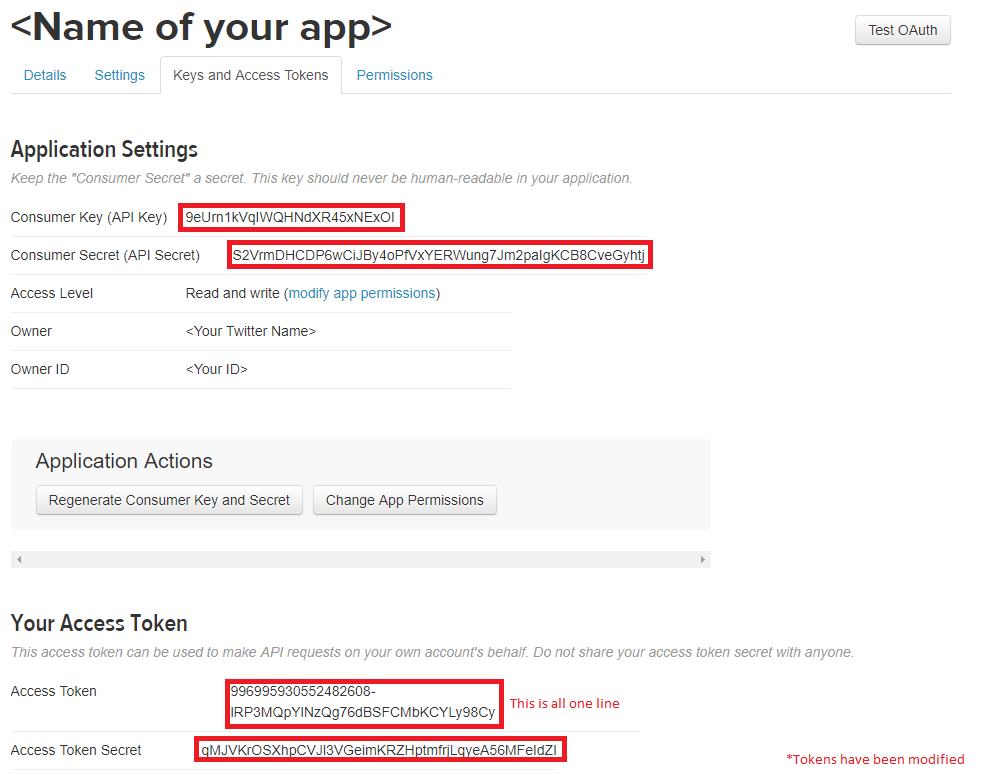
Save these somewhere for the next part of creating the bot.
Creating the Script
Now that everything is set up and we have the keys we need, we can make the script. Open IDLE, create a new script and save it as a .py.
First, we will want to import the tweepy module.
import tweepy
Now we will want to enter the keys we got from the newly created twitter app. Save them in four separate variables as shown below. Make sure to use your own keys.
consumer_key = '4z*********************oF'
consumer_secret = '6P**********************************************3T'
access_token = '79**********************************************nA'
access_token_secret = 'PS*****************************************dO'
Now we need to set up the twitter API by using OAuthHandler and API classes.
auth = tweepy.OAuthHandler(consumer_key, consumer_secret)
auth.set_access_token(access_token, access_token_secret)
api = tweepy.API(auth)
Next, we will set two simple variables. One will hold different search queries and the other will be max tweets per query. These will be used later. You can freely modify these later after you understand what they do (noted in "Running the Script").
queries = ["rt to win", "retweet to win"]
tweets_per_query = 50
Now set a variable to count the number of tweets re-tweeted to use at the end and create a loop looping through the queries declared previously.
new_tweets = 0
for query in queries:
In this for loop, print what query we are querying and then create another for loop that loops through tweets that are returned from the API search using the query in the current loop.
print ("Starting new query: " + query)
for tweet in tweepy.Cursor(api.search, q=query, tweet_mode="extended").items(tweets_per_query ):
Now inside this loop, we will focus on each individual tweet which is now in the 'tweet' variable.
Get the user's screen name that tweeted the tweet, id and then create and print the URL. This is mainly for output purposes but will be used later.
user = tweet.user.screen_name
id = tweet.id
url = 'https://twitter.com/' + user + '/status/' + str(id)
print (url)
Since we used the extended tweet_mode in the search query, we will be given all the text in the tweet rather than the normal 140 returned by the API.
This text will be sitting in tweet.retweeted_status.full_text if the tweet we are looking at is a re-tweeted tweet or in tweet.full_text if this is the original tweet. Convert the text to lowercase to make it easier to deal with later.
try:
text = tweet.retweeted_status.full_text.lower()
except:
text = tweet.full_text.lower()
Now we want to look at the text content of the tweet to decided what we need to do.
If the tweet contains the terms "retweet" or "rt", we need to retweet the tweet. To do this we need to use the .retweet() method and then add 1 to new_tweets. An error will occur if we have already tweeted the tweet so we must account for that.
if "retweet" in text or "rt" in text:
if not tweet.retweeted:
try:
tweet.retweet()
print("\tRetweeted")
new_tweets += 1
except tweepy.TweepError as e:
print('\tAlready Retweeted')
If the tweet contains the terms "like" or "fav" we need to favorite the tweet. Twitter has now called this "liking" a tweet but in the API it is still called favorite. So still in the tweet for loop:
if "like" in text or "fav" in text:
try:
tweet.favorite()
print('\t' + "Liked")
except:
print('\tAlready Liked')
If the tweet contains the term "follow" in it, we need to follow someone. Thankfully the API provides us with who is mentioned in the tweet so little work is done to extract people. Remember that some of these tweets will be re-tweeted tweets so we need to ignore the person that re-tweeted and get the original 'tweeter'. The following code should do the trick, using api.create_friendship to follow people.
if "follow" in text:
try:
to_follow = [tweet.retweeted_status.user.screen_name] + [i['screen_name'] for i in tweet.entities['user_mentions']]
# Don't follow origin user (person who retweeted)
except:
to_follow = [user] + [i['screen_name'] for i in tweet.entities['user_mentions']]
for screen_name in list(set(to_follow)):
api.create_friendship(screen_name)
print('\t' + "Followed: " + screen_name)
Lastly print a friendly message at the end saying how many tweets we re-tweeted to show that the script is finished. This is outside all loops.
print ("New Tweets: " + str(new_tweets))
Running the Script
To use this script, put queries you want to search for in the 'queries' list towards the top. Set tweets_per_query to how many tweets per query you want to loop at; remember too many interactions with the API and you may get restricted access due to usage limits. Also going back too far with large queries could potentially be an issue.
Now simply run the script by hitting F5 in IDLE or double-clicking on the script. Wait and you should see what the script is up to until it's done.
Final Script
import tweepy
consumer_key = '4z*********************oF'
consumer_secret = '6P**********************************************3T'
access_token = '79**********************************************nA'
access_token_secret = 'PS*****************************************dO'
auth = tweepy.OAuthHandler(consumer_key, consumer_secret)
auth.set_access_token(access_token, access_token_secret)
api = tweepy.API(auth)
queries = ["rt to win", "retweet to win"]
tweets_per_query = 50
new_tweets = 0
for query in queries:
print ("Starting new query: " + query)
for tweet in tweepy.Cursor(api.search, q=query, tweet_mode="extended").items(tweets_per_query ):
user = tweet.user.screen_name
id = tweet.id
url = 'https://twitter.com/' + user + '/status/' + str(id)
print (url)
try:
text = tweet.retweeted_status.full_text.lower()
except:
text = tweet.full_text.lower()
if "retweet" in text or "rt" in text:
if not tweet.retweeted:
try:
tweet.retweet()
print("\tRetweeted")
new_tweets += 1
except tweepy.TweepError as e:
print('\tAlready Retweeted')
if "like" in text or "fav" in text:
try:
tweet.favorite()
print('\t' + "Liked")
except:
print('\tAlready Liked')
if "follow" in text:
try:
to_follow = [tweet.retweeted_status.user.screen_name] + [i['screen_name'] for i in tweet.entities['user_mentions']]
# Don't follow origin user (person who retweeted)
except:
to_follow = [user] + [i['screen_name'] for i in tweet.entities['user_mentions']]
for screen_name in list(set(to_follow)):
api.create_friendship(screen_name)
print('\t' + "Followed: " + screen_name)
print ("New Tweets: " + str(new_tweets))
Final Notes
Unfortunately, I didn't add a "tag your friend" command because I didn't want to annoy anyone and didn't bother making another account. This could be a bit hard to implement because sometimes this is an arbitrary number requested.
I am not responsible for any harm that may come from this.